Statistics - Introduction
Basics
1. Mean, median, mode, and range.
- Mean: the average; the sum of the values divided by the number of values
Median: the middle number when the numbers are sorted in order
Mode: the most frequent number in a data set
Range: the difference between the highest value and the lowest value
Example: find the mean, median, mode, and range of the data set: 10, 14, 7, 23, 23, 15, 7, 23, 32.
Median: sort the date set from smallest to largest:7, 7, 10, 14, 15, 23, 23, 23, 32. So that the median of this data set is 15.
Mode: 7 appears twice, and 23 appears three times, so the number 23 is the mode of this data set.
Range: the highest number is 32, and the lowest one is 7. So the range = 32-7 = 25.
2. Quartile:
First quartile/Q1/lower quartile/25th percentile: the median of the lower half of the data set
Second quartile/Q2/middle quartile/medium
Third quartile/Q3/upper quartile/75th percentile: the median of the upper half of the data set
Interquartile range/IQR/midspread/middle 50%/H-spread: the difference between Q3 and Q1
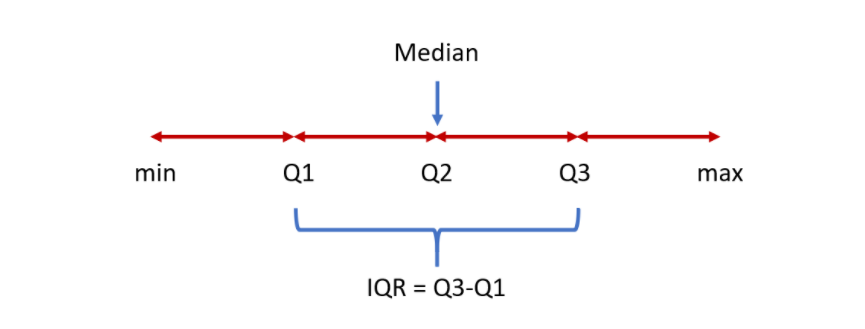
Example: find the Q1, Q2, Q3, and IQR of the data set: 5, 7, 8, 10, 11, 13, 14, 16, 16, 17, 27.
Q1 = 8, Q2 = 13, Q3 = 16, IQR = 16-8 = 8
3. Qualitative and Quantitative
Qualitative: express a qualitative attribute
Quantitative: can be measured in terms of numbers
4. Two important types of data sets: populations and samples
Populations: the entire set, includes all the elements
Sample: a subset of a population. Sample size is always less than the population size.
5. Parameters vs. Statistic
Statistic: a measurable characteristic computed from a sample of data
Parameter: a measurable characteristic computed from an entire population of data